Tech radar
Analysis of the Tech Radar
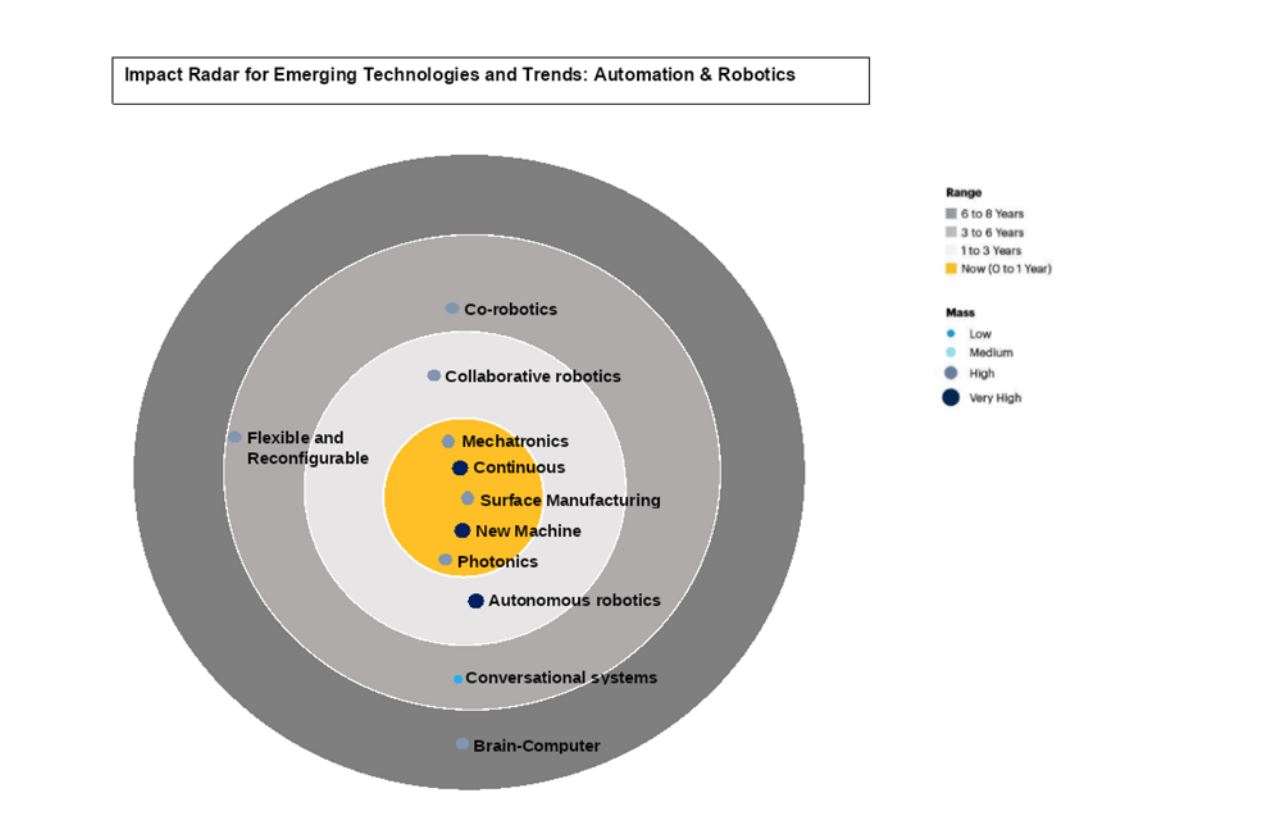
Source: Gartner Top Strategic Technology Trends for 2022
There are several significant emerging trends in the world of industrial automation and robots that have a big impact on a wide variety of industrial sectors.
1) Increasing ease of use, deployment and maintenance
Automation and Robotic technology has undergone various technological advances in the recent years. The robots are commonly used for the automotive industry but for industries that are relatively new to automation, programming robots are still a challenge. The fourth industrial revolution ”Industry 4.0″ that was referred to as high technology strategy that aims to automate and computerize complete industry or complete environment at the highest technological level. Now within the fifth industrial revolution the challenge is how to harmonize human-machine collaboration and support those SMEs which are still in process of targeting Industry 4.0 revolution to support them in complete digital transformation. Today more and more companies find that robots are within their affordability budgets. The challenge they have to overcome is ensuring complexity of programming and designing robotic systems as well as synchronization of the data. It also a question of highly skilled workforce to deploy, operate and maintain.
2) Human-Robot Collaboration
Collaborative robots are robots designed to work in direct human company. Equipped with a number of sensors and additional protective elements, they can work without fencing in the immediate vicinity of the operator. One of the advantages of such a robot is space saving and increased safety. For safety reasons, these robots operate at much lower speeds than conventional robots closed in fenced areas. An example of a collaborative robot is the Kawasaki Duaro equipped with two arms, which is used in applications requiring precision and the use of various tools – e.g. when assembling electronic systems that can be picked up by the operator directly from the robot for further processing or quality control. Close collaboration between humans and robots, working on assembly lines and in other applications, is already part of business operations.
3) New ways of working with robots
The next step in automation and robotics transformation is ensuring connectivity between human resources and robots that support them (and vice versa) and managing them from any device, anywhere with an Internet connection to simplify all stages of robot interaction (design, sales, installation, commissioning, operation, oversight, and service).
4) Improved ROI
Today’s modern industrial robots offer relatively quick return on investment. They reduce injuries in the workplace, increase the competitiveness of companies in a fierce global market, elevate the quality of affordable products, increase profits, and create a whole new ecosystem of high-paying jobs. Based on a huge body of evidence, experience and common sense, it is clear that the companies that adopt robots realize huge financial benefits in longer run. Integrating robots increase productivity, reduce overhead, provide flexibility, reduce waste, and increase quality.
5) Training the robot employees of the future
Industrial robots have created a whole new ecosystem of high paying and rewarding jobs. Designing, building, marketing, selling, installing, operating and maintaining robots creates jobs that didn’t exist before robots. Robots allow companies to remain cost competitive even while maintaining production in a high cost country as opposed to moving operations to a low cost country. This preserves jobs in the high cost countries that would otherwise be entirely shifted to the low cost countries.
Many companies are looking to automated systems for their warehouses and distribution centers.
For many companies automation is a key part of their business strategies. The pandemic accelerated the business case for full-enterprise automation solutions and, consequently, robotics-based solutions are more and more in usage.
- Robots don’t replace workers, they create opportunities in the area of highly accidental workplaces and where is long-term labour shortage.
- Robotic automation creates roles for workers in operation support and maintenance — higher paying, more rewarding jobs that can help companies attract and retain valued employees.
- Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) provide an excellent example of humans and robots interaction. AMRs safely coexist with dynamic features to navigate around people, equipment, and inventory, mainly transporting materials within a facility instead of conveyor or monorail. In this case, robotics become an extension of a successful work environment.
- The future with robotic applications, advancement in both productivity and safety depends on software, specifically developments in Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI). ML allows robotic systems to learn and adapt without following explicit instructions, but instead by using algorithms and statistical models to analyze and draw inferences from patterns in data. AI empowers robotics systems to improve by continuously fine-tuning operational processes.
- Software is the key to the future flexibility, so it’s vital for companies to have a partner – integrator who will be with them every step of the way — from design and implementation to operation and eventual upgrades.
Risk Heat Map
Within PLLs and TTTDM dedicated to CAMI4.0 Automation and Robotics, the consortium Project Partners have identified several risks and challenges:
- Managing large volumes of data
Managing large volumes of data can be difficult and time-consuming. The key to managing large volumes of data is data automation. The challenge which appear in the data automation is data quality and data accuracy.
- Ensuring and maintaining security and privacy
One of the challenges of adopting business process automation is keeping information and data flowing between departments inside organizations secure and maintaining a high level of information privacy without endangering the process being performed.
- Lack of skilled labour
One of the most significant challenges in process automation is the ability to have trained people that can complete the automation project on time while retaining high-quality outcomes. A shortage of trained resources will jeopardize project delivery and indirectly impair quality, lowering employee satisfaction.
- Lack of budget to invest in automation
There are many challenges that make harder implementation of A&R, especially for SMEs originating from some CE regions. These companies have limited resources and make mistake when deciding at random to invest in automation without understanding whole process. Harmonization of the automation process requires the employment of specialists capable to design the complex digital transformation business model, engage appropriate software in order to provide the flexibility and adaptations required to complete the tasks. Furthermore, in-house personnel must be trained on how to use these technologies to get the most out of them.
- Lack of time for continuous improvement
Organizations are always striving to improve their business processes and reduce costs. One way that organizations can do this is by having continuous improvement meetings and audits. However, many companies struggle with the time it takes to conduct these meetings and audits resulting in little to no improvements being made.
- Integration and compatibility of legacy systems
To fully automate a process, you must be able to integrate with the various business line applications used by your firm to complete the process cycle. Older systems do not allow for integration, thus you will almost certainly end up with human intervention and negating the objective of your aim being attempted.
- Change management
Today’s business world is constantly changing, and it takes an incredible amount of time for an organization to smoothly adapt to these changes. This is especially true when the company has a large number of employees, or when there are numerous departments with varying levels of influence. With this in mind, it can be difficult to keep up with all of the organizational changes happening around you.
- Lack of Stakeholders’ buy-in can badly affect the implementation
One of the most important challenges of business process automation is the lack of interest from stakeholders which can badly affect implementation. Without the buy-in of key stakeholders and employees, this process can be disrupted by a lack of understanding and resistance. to change.
- Cost and time for implementation
- Complexity of standardization and synchronization process
Business processes are the foundation of any business. Without them, it would be difficult to run a company. However, despite the importance of these processes, they often take up a significant amount of time and energy for organizations.
Future of robotics.
Trends 2022
Collaborative robotics. The change can be seen in factories: the demand for mobile robotics to work autonomously in warehouses, sharing space with operators, has multiplied exponentially.
Ease of use. Good news for end users. Simplifying the implementation of industrial robotics is another clear trend for 2022, although for Robotnik, this aspect has always been a priority. Software and hardware architecture work towards intuitive and simple configuration, installation and interface.
Artificial Intelligence, 5G, IoT. The maturation of these 3 technologies, among others, allows the development of more intelligent robots that perform more precise tasks.
Interoperability. The communication of different robots with each other -fleets of robots- and with other external systems, increases safety and productivity.
New industries are rapidly adapting to automation through robotic systems.
Contact
Krakow Technology Park sp. z o.o.
ul. Podole 60
30-394 Kraków, Poland