Tech radar
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is one of the most important digital topics of the future and has already become an everyday technology. AI applications support and advance industry, finance, logistics and transport, healthcare, trade, public administration, media and many more. AI applications offer great potential for business and academia, but still many companies face some challenges in AI adaption and need to catch up faster and wider when it comes to the application of AI in their businesses.
Artificial Intelligence is often perceived by the policy decision makers as a plug-and-play technology that provides an immediate return on investment. However AI deployment requires not only technologies and talents, but also relies on a company’s culture, structure and way of working that all need to be harmonized to create space and achieve a broad acceptance of AI.
Some general challenges in AI implementation from companies point of view:
- Work still viewed in isolation today should become interdisciplinary collaboration.
- Data and AI-driven insights broaden the relevant decision basis and enable the decision-making process to be a more informed one.
- It requires a mindset that’s open to change and agility, as well as experimental approaches.
The four technology trends in AI implementation include:
- Artificial intelligence (AI) developer toolkits, services, marketplaces and easy-to-use APIs are beginning to “democratize” AI.
- Growing AI adoption is beginning to shift business automation from process automation to intelligent business automation.
- Advanced hardware, innovative software techniques and micro-AI are accelerating Edge AI adoption moving more and more processing from the cloud to the edge.
- AI (advanced NLP) is actually starting to transform how humans and machines interact.
Analysis of the Tech Radar
Source: Gartner Top Strategic Technology Trends for 2022
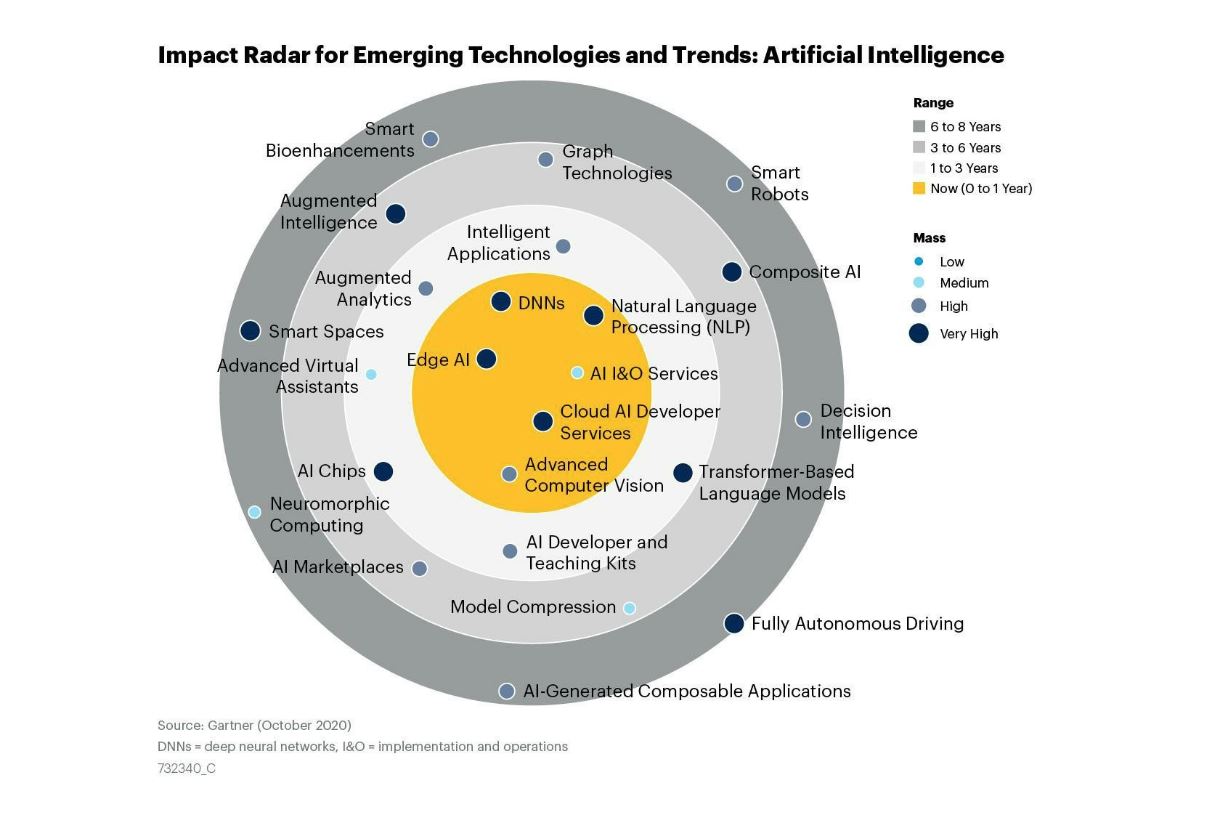
In the Artificial intelligence Trends Impact Radar, the rings represent the Range. Range estimates the distance (in years) that the technology or trend is from “crossing the chasm” from early-adopter to early majority adoption. The size and color of the emerging technology or trend radar blip represents its Mass. This indicates how substantial an impact the technology or trend will have on existing products and markets.
AI Developer and Teaching Kits
Artificial intelligence (AI) developer and teaching kits are instructions, examples, tools and software development kits (SDKs). They provide an abstraction layer on top of data science platforms, frameworks, analytic libraries and devices. And so they make it faster and easier for software engineers to build AI into applications.
These kits are 1 to 3 Years from early majority because they address a subset of needs including kits for virtual assistants, AI design kits, and AI-mobile-serving SDKs. Also, dependencies associated with vendor specific toolkit offerings limit usability. Additionally, there are challenges with scaling outputs and the cost of integrating different formats and interfaces across the stack.
Their impact mass is high because AI developer and teaching kits are a significant accelerator to AI adoption. This enables a much larger set of software developers to more effectively and efficiently contribute to AI development and implementation. Over the next three years, AI developer and teaching kits will provide a strong foundation for the expansion of more complex AI-enabled capabilities.
Transformer-Based Language Models
Transformer-based language models are DNNs that process words as sequences in a sentence. This approach preserves the context or meaning surrounding terms. It also substantially improves translation, transcription and natural language generation. These models are trained on enormous data sets of billions of phrases. Example transformer-based models include BERT, BART and GPT-3.
The 1-3 year range is driven by the effectiveness of the training tools, the runtime efficiency and the ease of deployment. Transformer-based language models such as GPT-3 have the capability to generate paragraphs of text that are indistinguishable from those written by a well-educated human.
The impact mass of transformer-based language models is very high because they are displacing RNN systems at a surprising rate. And new tools deliver substantial improvements in advanced text analytics and all the related applications such as conversational user interfaces, intelligent virtual assistants and automated text generation.
Intelligent Applications
Intelligent applications are enterprise business applications with embedded or integrated artificial intelligence technologies, such as intelligent automation, data-driven insights and guided recommendations. They represent a transformational shift in business applications from primarily procedural tools that help execute tasks to intelligent software that also assists in acquiring knowledge, visualizing key data and advising on relevant decisions.
Intelligent applications are 1-3 years from crossing the chasm because many of the large software vendors are now embedding AI into their products. And their efforts will create competitive momentum further driving adoption across application domains such as enterprise resource planning (ERP), sales force automation (SFA), HR and customer relationship management (CRM). Intelligent applications are the next major battleground for enterprise application providers and it will be many years before we hit the top of this s-curve.
The impact on existing technologies is high because it refactors enterprise applications. This is a competitive opportunity for new entrants into the market. It also creates potential for existing players to gain, or lose, market share as competitive advantage shifts to intelligent application capabilities.
AI-Generated Composable Applications
AI-generated composite applications build business applications using artificial intelligence to assemble application components (without human developer involvement) to meet new and even ad hoc business needs. Context-aware AI will detect a specific business need in response to a business situation and automatically assemble the application using packaged business capabilities (PBCs) as building blocks.
This technological capability is 6 to 8 Years from crossing the chasm because it is dependent on the emerging trend where technology providers shift from delivering large and mostly static business applications to offering smaller PBCs with robust application programming interfaces (API). Most of the technology already exists (e.g., APIs, microservices, self-integration, containerized software). But pulling it all together into a composable applications ecosystem with standards that facilitate interoperability is still a long way off. In this instance AI technology advancement is not the primary inhibitor.
AI-generated composable applications will have a high impact on the entire application software market and businesses across industries and geographies. They represent a substantial improvement in business agility allowing businesses to respond more quickly to changing technology and business situations. The entire business world will be able to move faster which can lead to even more rapid change across business and society.
Conclusions:
Artificial Intelligence has meshed into various industries. There is a significant increase in tools, applications, and platforms based on AI and Machine Learning (ML). These technologies have impacted healthcare, manufacturing, law, finance, retail, real estate, accountancy, digital marketing, and several other areas.
Companies are investing in AI research to find out how they can bring AI closer to humans. By 2025 AI software revenues alone will reach above $100 billion globally (Source: Tractica).This means that the advancement of AI and Machine Learning (ML)-related technology will be dominating in foreseeable future.
There are several significant emerging trends in AI that have a big impact on a wide variety of industrial sectors.
- Intelligent Process Automation
In the latest technology trend, organisations are looking for intelligent automation tools to solve business challenges and increase productivity, efficiency, and accuracy, benefiting the organisation. One of the successive waves, Intelligent Process Automation, or IPA, brings together Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies to empower rapid end-to-end business process automation and accelerate digital transformation. In RPA, computer software ‘robots’ handle repetitive, rule-based digital tasks which are driven by structured data. However, many business processes now are fed by or generate large amounts of unstructured and real-time data. IPA makes it possible to automate processes with machine learning and analytic capabilities and cognitive technologies, like computer vision, Natural Language Processing (NLP), and fuzzy logic. The adoption of IPA is expected to grow in the coming days, with large-scale growth expected across several industries.
- A Shift Toward Cybersecurity
With data becoming more precious than ever before, there’s no shortage of cyber criminals out there looking for new ways to compromise it. One of the downsides of novice-level AI is that hackers can manipulate them to access the sensitive information. So, a significant trend in AI is developing technology to recognise and report common types of attacks. Anti-virus software is also being developed by using AI in the same manner as this technology can help prevent a malware threat from having devastating consequences. When it comes to businesses, AI-powered cybersecurity tools also can gather data from a company’s own communications networks, digital activity, transactional systems, and websites, as well as other external public sources. These tools then run algorithms to identify patterns and detect or predict threatening activity, potential data breaches, etc. This is a trend we can expect to continuously see in the future as criminals constantly create new malware and data acquisition methods.
- AI for Personalised Services
As AI becomes more powerful and efficient at researching a particular market and demographic, acquiring consumer data is becoming more accessible than ever. The biggest AI trend in marketing is the increasing focus on providing personalised services. One of the most common ways that AI can do so is through analysing the online activity of individuals who search for specific keywords. This level of personalisation is virtually guaranteed to provide a better experience for customers, which will directly increase the revenue of companies that take advantage of it. As machine learning becomes more adept at understanding what people want in specific instances, AI will become less of a sales tool and more of a digital friend.
- Automated AI Development
In coming years, expect to see significant innovations in the area of ‘AI for AI’: using AI to help automate the steps and processes involved in the life cycle of creating, deploying, managing, and operating AI models. At a certain level, AI can develop its algorithms to solve problems, increase efficiency, and provide humans with useful research data.
Using automated AI will allow even non-experts to use AI algorithms and techniques. One example is Google’s AutoML, a tool that simplifies creating machine learning models and makes the technology accessible to a wider audience. These tools can create as much customisation as required without knowing the complex workflow of Machine Learning in detail. Although this type of development is in infancy, automated AI is renowned for growing exponentially and is a major AI trend.
- Autonomous Vehicles
With companies like Samsung, Nvidia, Volkswagen, Uber, and Google’s Waymo, the scope of autonomous driving has increased many folds. Everyone knows AI’s functionality into autonomous vehicles, and to tap such immense potential, car, and tech companies are infusing billions of dollars in this domain. The process is driven by the economic and social benefits involved. Car manufacturers hope that autonomous driving technology will sway consumers’ minds. Supporters believe that self-driving car technology will reduce traffic deaths and be a safe alternative to drive.
- Incorporating Facial Recognition
Facial recognition appears to be en vogue at the moment. It is popping up in many aspects of our lives and is being adopted by private and public organisations for various purposes, including surveillance. More countries are readying themselves to incorporate facial recognition technology and enhance their security measures. Deep learning algorithms are being set to ensure that this technology goes beyond regular facial recognition and more understanding images and scenarios. It will also help provide more personalised communications to customers, making it a notable AI trend for coming years.
- Convergence of IoT and AI
The lines between AI and IoT are increasingly blurring. While both technologies have independent qualities, used together, they are opening up better and more unique opportunities. The Internet of Things (IoT) devices create a lot of data that needs to be mined for actionable insights. On the other hand, Artificial Intelligence algorithms require the data before making any conclusions. So the data collected by IoT is being used by AI algorithms to create valuable results that are further implemented by the IoT devices. AI’s ability to rapidly glean insights from data makes IoT systems more intelligent. In upcoming years more than 80% of enterprise IoT projects will incorporate AI in some form, up from just 10% today.
- AI in Healthcare
The contributions that AI can import to the healthcare industry are working in groundbreaking ways, allowing people worldwide to receive safer and more efficient care and making it easier to detect, prevent, and cure diseases. Also, AI’s ability to acquire data in real-time from electronic health records, emergency department admissions, equipment utilisation, staffing levels, etc. – and to interpret and analyse it in meaningful ways enables a wide range of efficiency and care-enhancing capabilities in hospital administration. Drug discoveries are another field where AI is acerbating.
AI is playing an essential role in helping healthcare professionals respond to the coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak. AI is being used to distinguish COVID patients and essential hot spots. COVID vaccine drug discovery is being repurposed and speeded up using AI techniques. Researchers have developed AI-based thermal cameras and smartphone apps for estimating the temperature of people and assembling data for healthcare organisations. Intelligent robots are being deployed to implement “contactless delivery” for isolated individuals, helping medical staff ensure that the key areas stay disinfected and safe for use.
- Augmented Intelligence
For those who may still be worried about AI cannibalising their jobs, the rise of AI should be a refreshing trend. It brings together the best capabilities of both humans and technology, giving organisations the ability to improve their workforce’s efficiency and performance. By 2023, Gartner predicts that 40% of infrastructure and operations teams in large enterprises will use AI-augmented automation, resulting in higher productivity. The healthcare, retail, and travel industries have already created uses of Augmented Reality. Therefore, following this AI trend, there will be an increase in the number of augmented reality apps.
- Explainable AI
Despite becoming so ubiquitous, AI has suffered from trust issues. Much of what machine learning accomplishes becomes unknowable at various points of the process and appears as a black box. It’s often impossible to explain how the AI came to an inevitable conclusion. Explainable AI is designed to simplify and visualise how ML networks make decisions. There is a more significant push for deploying AI in a transparent and clearly defined manner. While companies will make efforts to understand how AI models and algorithms work? AI/ML software providers will make sophisticated ML solutions more explainable to users.
- Ethical AI
Rising demand for ethical AI is at the top of the list of emerging technology trends. In the past, organisations that adopted Machine Learning and other Artificial Intelligence technologies were not much preoccupied with their ethical impact. Today, however, values-based consumers and employees expect companies to adopt AI responsibly. Over the next few years, firms will deliberately choose to do business with partners that commit to data ethics and adopt data handling practices that reflect their values and customers’ values.
Risk Heat Map
Within PLLs and TTTDM dedicated to CAMI4.0 Artificial Intelligence, the consortium Project Partners have identified several challenges:
- Managing large volumes of data
The collection of large amounts of data linked with AI applications can be used for trying to predict future business and individual behavior scenarios.
- Lack of AI implementation traceability and Data sourcing
Traceability is considered a key requirement for trustworthy artificial intelligence (AI), related to the need to maintain a complete account of the provenance of data, processes, and artifacts involved in the production of an AI model. However quite often AI is increasingly being implemented outside the official IT team, which makes all process of AI implementation traceability complex and fragmented. Moreover managing large volumes of data can be difficult and time-consuming and AI’s reliance on big data is already impacting privacy in a major way. The key to managing large volumes of data is data automation. The challenge which appear in the data automation is data quality and data accuracy.
- Introducing Program Bias into decision making processes
One of the more damaging risks of artificial intelligence is introducing bias into decision-making algorithms. AI systems learn from the dataset on which they were trained, and depending upon how this compilation occurred there is potential for the dataset to reflect assumptions or biases. These biases could then influence system decision making.
Violation of personal privacy
The proper regulations and self-imposed limitations should be introduced into business and individual relations. Respect to human values, including privacy if not controlled and monitored it can have a negative impact on personal privacy and the right to freedom from discrimination. There is a high real risk that commercial and state use will have a detrimental impact on human rights due to wide AI applications tracking humans.
- Lack of transparency
One of the challenges of adopting wider AI applications and technologies is keeping personal data safe and secure with high level of data anonymization if required and maintaining a high level of information privacy without uncontrolled leaks or due to exposition to cyber-attacks.
- Black Box Algorithms and Lack of Transparency
The primary purpose of many AI systems is to make predictions, and as such the algorithms can be so inordinately complex that even those who created the algorithm cannot thoroughly explain how the variables combined together reach the resulting prediction. This lack of transparency is the reason why some algorithms are referred to as a “black box,” and why legislative bodies are now beginning to investigate what checks and balances may need to be put in place.
- Lack of time for continuous improvement
Organizations are always striving to improve their business processes and reduce costs. One way that organizations can do this is by having continuous improvement meetings and audits. However, many companies struggle with the time it takes to conduct these meetings and audits resulting in little to no improvements being made.
- Integration and compatibility of legacy systems
To take benefits of AI technology and application partially or fully introduced into business, the company must be able to integrate with the various business line applications used internally to complete the process cycle.
- Unclear Legal Responsibility
Future of AI.
Trends 2022
AI is important because it forms the very foundation of computer learning. Through AI, computers have the ability to harness massive amounts of data and use their learned intelligence to make optimal decisions and discoveries in fractions of the time that it would take humans.
AI will continue to have huge impact on future industries:
Manufacturing: AI powered robots work alongside humans to perform a limited range of tasks like assembly and stacking, and predictive analysis sensors keep equipment running smoothly.
Transportation: Although it could take some time to perfect them, autonomous cars will one day ferry us from place to place.
Healthcare: In the comparatively AI-nascent field of healthcare, diseases are more quickly and accurately diagnosed, drug discovery is sped up and streamlined, virtual nursing assistants monitor patients and big data analysis helps to create a more personalized patient experience.
Education: Textbooks are digitized with the help of AI, early-stage virtual tutors assist human instructors and facial analysis gauges the emotions of students to help determine who’s struggling or bored and better tailor the experience to their individual needs.
Media: Journalism is harnessing AI, too, and will continue to benefit from it. Bloomberg uses Cyborg technology to help make quick sense of complex financial reports. The Associated Press employs the natural language abilities of Automated Insights to produce 3,700 earning reports stories per year — nearly four times more than in the recent past.
Customer Service: AI in customer service is now more than a buzzword – it’s becoming a must-have. AI can be in the form of customer support chatbots, customer self-service, machine learning to analyze customer data, natural language processing for speech recognition and support, and many other potential use cases.
Contact
Krakow Technology Park sp. z o.o.
ul. Podole 60
30-394 Kraków, Poland